INTRODUCTION:
Intellectual property rights (IPR) include the legal protection afforded to the creations or inventions of individuals or organizations. These rights provide exclusivity and control over the use of intellectual property and foster innovation, creativity, and economic development.
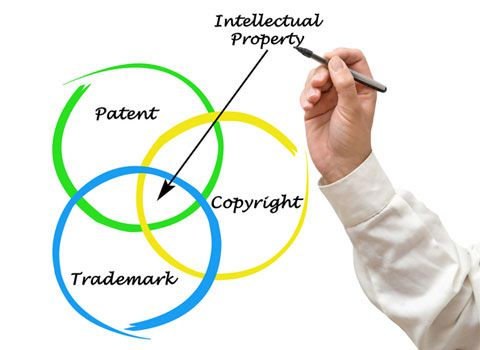
Intellectual property comes in many forms, and IPR aims to strike a balance between fostering innovation and ensuring fair competition.

Main Types of Intellectual Property:
1. Patents:
Give inventors exclusive rights to new and useful inventions and prevent others from making, using, or selling the patented invention without permission.
2. Trademark:
Protects distinctive signs, symbols, names, and identifiers used in commerce to distinguish goods and services.
Trademarks establish brand identity and prevent confusion in the marketplace.
3. Copyright:
Protects original copyrighted works, including literature, music, art, and software.
Copyright law grants authors the exclusive right to reproduce, distribute, and display their works.
4. Trade Secrets:
Protect confidential and proprietary information such as formulations, processes, and customer lists that provide a competitive advantage.
Unlike other forms of intellectual property, trade secrets are not publicly available.
5. Design:
Covers the visual appearance of a product, including its shape, composition, and decoration.
Design rights protect the aesthetics and visual characteristics of a product.
Intellectual property is a worldwide concern, and various international treaties and agreements regulate its protection.
The Main organizations are:
1. World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO):
WIPO is a specialized agency of the United Nations that promotes cooperation and development of intellectual property policies around the world.
2. Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS):
A World Trade Organization (WTO) agreement establishing minimum standards for the protection of intellectual property in member countries.
Importance of IPR:
1. Promoting Innovation: IPR provides financial incentives to inventors and creators by granting exclusive rights.
This fosters innovation, research and development of new products and technologies.
2. Promoting economic growth: Intellectual property contributes significantly to economic growth by fostering a culture of innovation and creativity.
This allows companies to monetize their inventions and creations.
3. Consumer Protection: Trademarks and other intellectual property rights help consumers make informed decisions by ensuring the quality and origin of products and services.
4. Promoting fair competition: IPR creates a framework for fair competition by preventing the unauthorized use of inventions and creations, thereby protecting investments by innovators.
5. Cultural Development: Copyright protection supports the development of literature, art, and culture by giving authors the opportunity to control and earn income from their works.

Challenges of IPR:
1. Balancing access and incentives: Finding the right balance between providing incentives for creators and ensuring public access to knowledge and technology is an ongoing challenge.
2. New Technologies: The digital age brings challenges, especially in issues such as online piracy, digital rights management, and software and algorithm protection.
3. Access to Medicines: There is an ongoing debate about the trade-off between protecting pharmaceutical patents and ensuring affordable access to medicines, especially in developing countries.
Understanding and managing the complexities of intellectual property rights is critical for individuals, businesses, and policy makers in today’s knowledge economy.
The legal framework for intellectual property rights aims to create an enabling environment for innovation and creativity, taking into account the interests of creators, consumers and society as a whole.
Emerging Trends in IPR:
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
The increasing use of AI and machine learning is creating challenges for protecting intellectual property.
Topics include determining ownership of AI-generated inventions and addressing AI’s role in the creation and infringement of copyrighted works.
2. Digital Transformation and Blockchain:
Blockchain technology is being researched for the protection and management of intellectual property assets.
It provides a decentralized and tamper-proof way to record and verify IP transactions, with potential implications for areas such as patent filing, copyright protection, and supply chain management.
3. Open Source and Collaborative Innovation:
Open source software and collaborative innovation models are becoming increasingly important.
Businesses use open source projects strategically while managing associated license risks and compliance.
4. Green Technology and Sustainable Innovation:
The field of green technology and sustainable innovation is increasingly focused on protecting intellectual property.
More and more companies are filing patents related to renewable energy, environmentally friendly processes, and sustainable practices.
5. Privacy and Security:
As data becomes a valuable asset, it becomes increasingly important to protect intellectual property related to data, algorithms, and software.
The interface between data protection law and intellectual property rights, particularly as it relates to personal data, is an evolving area.
6. Remote Collaboration and IP Challenges:
The transition to remote work has created challenges related to IP protection.
Topics include securely managing sensitive information, tracking IP contributions in virtual environments, managing potential compromise risks, and more.
7. Innovations in Biotechnology and Life Sciences:
Advances in biotechnology, such as gene editing and personalized medicine, bring new intellectual property challenges and opportunities.
Patent offices are adapting to the increasing complexity of biotechnology inventions.
8. Protecting Trade Secrets:
As the workforce becomes more mobile, protecting trade secrets has become a priority.
Companies implement sound strategies to protect trade secrets, such as the use of non-disclosure agreements and employee training programs.
9. Global harmonization of intellectual property law:
Efforts continue to achieve global harmonization of intellectual property law based on international agreements and treaties.
This trend aims to streamline procedures and create a more consistent framework for intellectual property protection across jurisdictions.
10. Pharmaceutical Patent Landscape:
The pharmaceutical industry is experiencing a shift in patent strategy, with an emphasis on personalized medicine, biologics, and addressing challenges related to patentability and regulatory compliance.
11. Intellectual Property Rights Enforcement in E-Commerce:
The growth of e-commerce has created major challenges in intellectual property enforcement, including combating counterfeit goods, online piracy, and protecting trademarks in digital markets.
12. Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality (AR/VR):
The development and commercialization of AR and VR technologies presents new challenges for intellectual property protection, including issues related to virtual goods, user interfaces, and immersive experiences.
Staying on top of these emerging trends is critical for businesses, legal professionals, and policy makers to navigate the evolving intellectual property landscape.
As these trends continue to shape the sector, proactive strategy and adaptability are key to effectively managing and protecting intellectual property.

Insights from India’s leading Intellectual Property Lawyers:
1. Increasing importance of intellectual property in business strategy: Indian companies, both large and start-ups, are increasingly recognizing the strategic value of intellectual property.
Intellectual property was seen not only as a legal necessity but also as an important part of business strategy contributing to competitiveness and market position.
2. Increased Awareness of Enforcement Strategies: IP lawyers focus on developing effective enforcement strategies for their clients.
This aimed not only to secure intellectual property rights through registration, but also to actively monitor and enforce these rights to prevent infringement.
3. The Rise of Specialist IP Law Firms: Specialist IP law firms are becoming increasingly important, offering a full range of services focused solely on intellectual property.These companies often have experts in various fields such as patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets.
4. Patent Prosecution Challenges: Managing the complex patent prosecution process has been a challenge in the patent field, especially in emerging areas such as biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and information technology.The landscape was changing due to changes in patent examination standards and an increased emphasis on innovation.
5. Brand Protection and Brand Strategy: Brand protection was a key focus and our attorneys helped our clients develop a strong brand strategy.
The rise of e-commerce and digital markets has highlighted the importance of brand protection in the online space.
6. International cooperation and filing: Many IP lawyers have been actively involved in promoting international cooperation and filing strategies.Given the global nature of the business, the customer sought protection for its intellectual property in multiple jurisdictions.
7. Concerns about counterfeiting and piracy: The fight against counterfeiting and piracy remained a major concern.
Intellectual property attorneys have been involved in developing and implementing anti-counterfeiting strategies, particularly in industries such as pharmaceuticals, consumer goods, and luxury goods.
8. Influence of case law: Important court decisions continued to shape the interpretation and enforcement of intellectual property law.
Lawyers have closely tracked and analyzed decisions affecting patentability, trademark distinctiveness, and copyright infringement.
Analysis of emerging trends in IPR and how top firms are adapting:
1. Digital Transformation and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Trend: The increasing integration of AI and digital technologies into various industries presents challenges and opportunities for intellectual property rights.
These include issues related to patentability, ownership, and infringement of AI-generated innovations.
Adaptation: Leading companies are likely to invest in expertise related to AI and digital technologies.
This includes staying abreast of legal developments, participating in policy discussions, and providing tailored services to clients working on AI innovation.
2.Remote Work and Collaboration: Trends: The increase in remote work has implications for the protection of intellectual property, particularly the protection and management of confidential information and trade secrets in distributed work environments.
Adaptation: companies can adapt by providing remote collaboration guidance, implementing secure communication tools, and helping customers develop policies to protect intellectual property assets in virtual work environments.
3. Harmonization with Globalization: Trend: Globalization of markets requires a strategic approach to intellectual property protection across multiple jurisdictions.
The harmonization effort aims to streamline processes and create a more consistent framework for intellectual property protection around the world.
Adaptation: Top companies may expand their international operations, collaborate with overseas counterparts, and advise clients on global IP strategies.
This includes regulating international treaties, managing cross-border intellectual property disputes, and ensuring compliance with various legal frameworks.
4. Open Source and Co-Innovation: Trends: Open Source Software and Co-Innovation Models Are Increasingly Important and Require a Differentiated Approach to Intellectual Property Protection, Licensing, and Compliance .
Adaptation: For leading companies that provide professional services related to open source licenses, perform IP audits for clients involved in collaborative projects, and provide guidance on resolving the complexities of shared intellectual property.
5. Biotechnology and Pharmacy: Trends: Advances in biotechnology and personalized medicine bring new challenges and opportunities related to patentability, regulatory compliance, and protection of innovations in the life sciences.
Adaptation: Top law firms have the potential to develop expertise in biotechnology and drug patent law, keep pace with regulatory changes, and help clients navigate the complexities of an evolving landscape.
6. Sustainability and Green Technology: Trend: A focus on sustainability drives innovation in green technology.
This includes the development and protection of inventions related to renewable energy, environmentally friendly processes and sustainable practices.
Adaptation: Leading companies may expand their practices to address the IP aspects of green technologies, advise clients on patent strategies in the sustainable sector, and contribute to the development of environmental IP policies .
7. E-commerce and brand protection: Trend: The growth of e-commerce is increasing the importance of online brand protection, combating counterfeit goods, and addressing intellectual property challenges in digital markets.
Adaptation: Leading companies may be improving their online brand protection capabilities, conducting digital IP audits, and helping clients enforce their rights in the digital space.
8. Privacy and Cybersecurity: Trend: The intersection of intellectual property, privacy and cybersecurity is becoming increasingly important as organizations focus on protecting valuable data and complying with data protection regulations.
Adaptation: companies have the potential to integrate privacy and cybersecurity expertise into their intellectual property practices, providing comprehensive advice on protecting intellectual property assets while ensuring compliance with data protection laws.

FAQ in trends in IPR:
1. Q: What are the current trends in intellectual property rights (IPR)?
A: Emerging trends in intellectual property rights include artificial intelligence, digital transformation, globalization, and innovation sustainability.
, including the impact of challenges related to remote work and collaboration.
2. Q: How are leading law firms adapting to digital transformation in the intellectual property space?
A: Leading law firms are adapting to digital transformation by investing in AI expertise, providing advice on remote collaboration, and expanding international practices to accommodate the global nature of digital innovation.
3. Q: What role does open source play in IPR trends?
A: Open source is gaining momentum and law firms are seeking professional services related to open source licensing.
He provides services, conducts IP reviews for collaborative projects, and advises clients on navigating the complexities of shared intellectual property.
4. Q: How are law firms addressing the intellectual property challenges of remote work?
A: Law firms are providing advice on remote collaboration and implementing secure communication tools We are adapting to this situation by helping our clients develop policies to protect their intellectual property assets in virtual work environments.
5. Q: What are the main challenges and opportunities in biotechnology and intellectual property rights?
A: Advances in biotechnology are creating challenges and opportunities related to patentability, regulatory compliance, and protection of innovation.
The law firm has strengthened its expertise in biotechnology patent law to help clients navigate the evolving landscape.
6. Q: How are law firms contributing to sustainability in the field of intellectual property rights?
A: Leading law firms are addressing the intellectual property aspects of green technology. We have expanded our practice, advising on sustainability patent strategies and contributing to the development of environmental intellectual property policy.
7. Q: How does e-commerce affect brand protection in the field of intellectual property rights?
A: The growth of e-commerce has increased the importance of online brand protection.
Law firms are improving their online brand protection skills, conducting digital IP audits, and helping clients enforce their rights in digital markets.
8. Q: How are data protection and IPR trends related?
A: Intellectual property, data protection, and cybersecurity are becoming increasingly important.
The law firm integrates privacy and cybersecurity expertise into its intellectual property practice, providing comprehensive advice on protecting intellectual property assets while ensuring compliance with data protection laws.
9. Q: How can companies adapt to globalization trends in the field of intellectual property rights?
A: Companies should seek advice from law firms with international experience and Adapt by registering your intellectual property rights in multiple jurisdictions and ensuring compliance with global intellectual property contracts and agreements.
10. Q: Are there any particular trends in IP litigation?
A: Trends in intellectual property litigation include increased enforcement in the digital space, strategic use of cease and desist letters, and a focus on resolving disputes related to emerging technologies such as AI and biotechnology.