
The diverse world of legal advocacy is a realm where professionals champion justice and navigate the complexities of the law, to protect the rights and interests of their clients. Advocates play a crucial role in our legal system, and their specialization often reflects the unique challenges they tackle.
Firstly, we have Trial Advocates, individuals who thrive in the courtroom, presenting compelling cases before judges and juries. These skilled litigators are adept at the art of persuasion, articulating their clients’ positions with clarity and conviction.
On the other side of the legal spectrum, we find Transactional Advocates. These professionals focus on preventing legal disputes before they arise. They excel in drafting contracts, negotiating deals, and providing strategic counsel to ensure their clients navigate the complexities of business and transactions smoothly.
In the realm of social justice, Public Interest Advocates dedicate their careers to representing individuals or groups who may not have the means to secure legal representation. Their work often involves addressing systemic issues, advocating for policy changes, and promoting access to justice for all.
For those navigating the intricacies of family law, Family Advocates step in. Their expertise extends to matters such as divorce, child custody, and spousal support, where empathy and understanding are as essential as legal proficiency.
Additionally, we have Environmental Advocates, who passionately advocate for the protection of our planet. Whether it’s challenging environmental violations or promoting sustainable practices, these advocates work towards a greener, more sustainable future.
Finally, in the ever-evolving digital landscape, Technology Advocates are emerging as key players. They specialize in navigating the legal complexities of the digital world, addressing issues such as cybersecurity, data privacy, and intellectual property in our technology-driven society.
These are just a few snapshots of the diverse roles advocates play in our legal ecosystem. Each type of advocate brings a unique set of skills and expertise to the table, contributing to the rich tapestry of our legal profession. Today, we’ll delve deeper into the fascinating world of advocacy and explore the nuances of each specialization.”
A lawyer is a professional who is trained and licensed to practice law, providing legal advice and representing clients in legal matters. The term “lawyer” is a broad and general one, encompassing various types of legal professionals, including attorneys, advocates, solicitors, and barristers, depending on the jurisdiction.

Key aspects of lawyers
- Legal Education:
- Lawyers typically undergo a formal legal education, obtaining a law degree from a recognized law school or university. The specific degree may vary by jurisdiction (LLB in many Commonwealth countries).
- Aspiring advocates typically pursue a law degree (LLB) from a recognized law school or university. After completing their legal education, they may enroll with the Bar Council of India, the regulatory body for legal practitioners in the country.
Also read AIBE Syllabus: Key Topics and Preparation Hacks
- Licensing and Admission to the Bar: After completing their legal education, individuals aspiring to become lawyers must usually pass a bar examination or meet other requirements set by the legal regulatory authority in their jurisdiction. Upon successful completion, they are admitted to the bar and become eligible to practice law.
Read Cracking AIBE: Essential Topics and Study Plan for Aspirants
- Roles and Responsibilities: Lawyers play various roles, including providing legal advice, drafting legal documents, negotiating on behalf of clients, and representing clients in court. Their responsibilities may vary depending on their specialization and the nature of legal issues they handle.
- Specializations: Lawyers often specialize in specific areas of law, such as criminal law, civil law, family law, corporate law, environmental law, intellectual property law, and more. Specialization allows lawyers to develop expertise in particular legal domains.
Read Career Guide: Opportunities In Intellectual Property Law With India’s Best Firms
- Ethical Standards: Lawyers are expected to adhere to high ethical standards in their practice. They owe a duty of loyalty and confidentiality to their clients and are obligated to act in the best interests of their clients within the bounds of the law.
- Advocacy and Representation: One of the primary functions of lawyers is to represent their clients in legal proceedings. This may involve presenting cases in court, negotiating settlements, and ensuring that clients’ rights are protected.
- Legal Research and Analysis: Lawyers engage in extensive legal research to understand relevant laws, regulations, and precedents that may apply to their clients’ cases. They analyze legal issues and apply the law to specific factual situations.
- Continuing Legal Education: Lawyers often engage in continuing legal education to stay updated on changes in the law and legal practices. This helps them maintain their professional competence throughout their careers.
- Legal Aid and Pro Bono Work: Some lawyers provide legal services to those who cannot afford representation, either through legal aid organizations or by taking on pro bono cases as a form of community service.
- Bar Council of India: The Bar Council of India is responsible for regulating legal education and the legal profession in the country. Advocates need to be registered with the respective State Bar Councils, which are subordinate bodies to the Bar Council of India.
Also read AIBE Syllabus: Key Topics and Preparation Hacks
- Enrollment and Advocates’ Roll: Upon completion of their legal education, aspiring advocates need to pass a bar exam conducted by the Bar Council of India. Once they pass the exam, they are enrolled as advocates, and their names are entered into the Advocates’ Roll maintained by the State Bar Council.
- Advocates Act, 1961: The legal profession in India is governed by the Advocates Act, 1961. This legislation outlines the rights and duties of advocates, the procedure for admission to the bar, and the regulatory framework for legal practice.
The term “lawyer” is used broadly, and the specific titles and roles may vary from one jurisdiction to another. For example, in some jurisdictions, the terms “attorney” or “advocate” may be more commonly used than “lawyer.”
Types of lawyers in India

In India, there are various types of lawyers who specialize in different areas of law to cater to the diverse legal needs of individuals, businesses, and organizations. Here are some common types of lawyers in India:
- Civil Lawyers: Civil lawyers handle cases related to civil law matters, such as property disputes, family disputes, contract disputes, and other non-criminal issues. Handle cases related to civil law, which includes disputes between individuals or organizations. This may involve matters such as property disputes, contract disputes, and family law issues.
- Criminal Lawyers: Criminal lawyers specialize in criminal law and defend individuals accused of committing crimes. They may work as public defenders or private attorneys. Specialize in criminal law and represent individuals accused of committing crimes. They may work as defense attorneys or prosecutors.
- Family Lawyers: Family lawyers focus on legal matters related to family relationships, including divorce, child custody, adoption, and domestic violence cases. Deal with legal issues related to family matters, such as divorce, child custody, adoption, and domestic violence cases.
- Corporate Lawyers: Corporate lawyers, also known as business lawyers, deal with legal issues related to business and corporate entities. They handle matters such as contracts, mergers and acquisitions, corporate governance, and compliance. Focus on legal matters related to business and corporate entities. They may handle contract negotiations, mergers and acquisitions, compliance issues, and other corporate legal matters.
- Labor Lawyers: Labor lawyers specialize in employment and labor law. They handle issues related to workplace disputes, employee rights, industrial disputes, and labor union matters. Specialize in issues related to employment and labor laws. They may handle cases involving workplace discrimination, harassment, wrongful termination, and labor union disputes.
- Real Estate Lawyers: Real estate lawyers deal with legal matters related to property and real estate transactions. They help with property transactions, land disputes, and issues related to property ownership and development. Handle legal matters related to real estate, such as property transactions, land disputes, and issues related to property ownership.
- Intellectual Property Lawyers: Intellectual property (IP) lawyers specialize in protecting and enforcing intellectual property rights, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Specialize in protecting intellectual property rights, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets.
Read Career Guide: Opportunities In Intellectual Property Law With India’s Best Firms
- Constitutional Lawyers: Constitutional lawyers focus on matters related to constitutional law. They may deal with issues such as fundamental rights, constitutional challenges, and matters related to the interpretation of the Indian Constitution. Focus on constitutional law and may be involved in cases related to constitutional rights, public interest litigation (PIL), and issues pertaining to the interpretation of the Constitution.
- Environmental Lawyers: Environmental lawyers handle legal issues related to environmental protection, conservation, and sustainability. They may be involved in cases related to pollution, conservation of natural resources, and environmental regulations.
- Tax Lawyers: Tax lawyers specialize in tax law and assist individuals and businesses in matters related to taxation. They may provide advice on tax planning, represent clients in tax disputes, and ensure compliance with tax laws.
- Human Rights Lawyers: Human rights lawyers work to protect and promote human rights. They may be involved in cases related to civil liberties, discrimination, and human rights violations.
- Consumer Protection Lawyers: Consumer protection lawyers advocate for the rights of consumers. They handle cases related to product liability, unfair trade practices, and consumer rights.
- Immigration Lawyers: Assist individuals and businesses with immigration-related legal matters, including visas, work permits, and citizenship applications.
- Cyber Lawyers: Specialize in handling legal issues related to cybercrime, internet law, and technology-related matters.
- Dispute Resolution Lawyers: Specialize in alternative dispute resolution mechanisms such as arbitration and mediation, offering a non-courtroom approach to dispute resolution.
- Government lawyers: A professional who works for the government is known as a Government Lawyers. They are trained certified lawyers who offers legal counsel to government ministers and administrative personnel. A government lawyer is in charge of addressing a variety of duties, including prosecuting criminal offences, making regulations, counselling local authorities, and resolving policy matters. In addition to advising government officials on a variety of legal matters, they also represents the government in court. They assist numerous government entities while also upholding local and municipal laws.
- Securities lawyer: Securities attorneys represent clients with respect to stocks, mutual funds, bonds, and other financial instruments. This work is primarily divided into three broad areas—transactional practice, regulatory practice, and litigation.Securities lawyers also frequently represent corporate clients in the transactional work involved with initial public offerings, private sales of securities, issuance of stock or other securities and mergers and acquisitions. In this capacity, they also assist companies in complying with securities laws and regulations, which ultimately serve to benefit consumers.
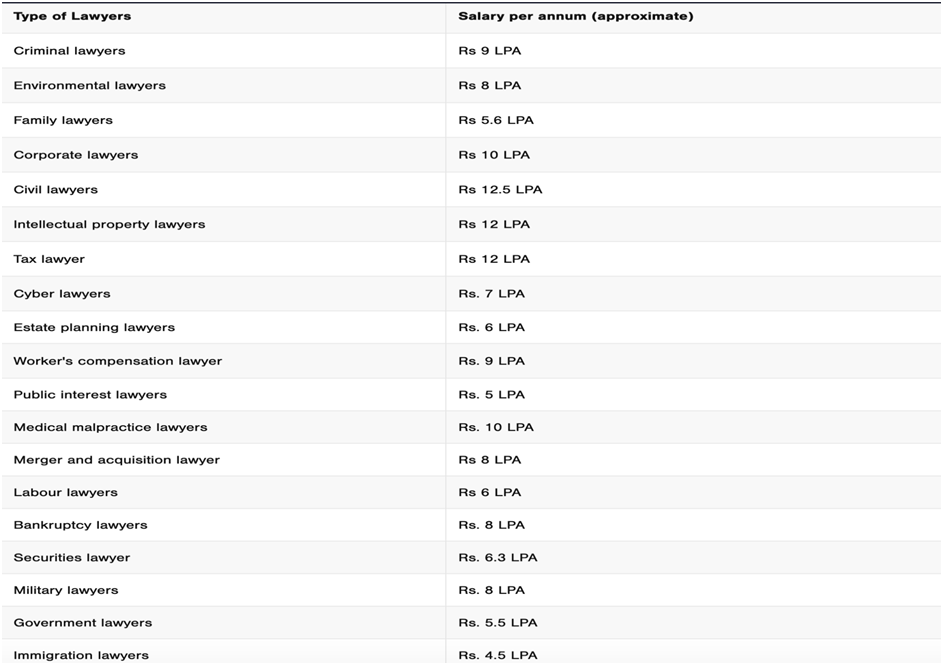
Salary of Advocates
Delving into the world of legal professions, it’s not just the pursuit of justice that varies but also the financial landscapes that distinguish one type of advocate from another. The legal field is vast and diverse, and with that diversity comes a spectrum of salaries reflective of the unique skills, expertise, and demands associated with each specialization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the diverse landscape of legal practitioners we’ve explored today reflects the complexity and richness of the legal profession. From Trial Advocates who passionately argue their cases in courtrooms to Transactional Advocates who craft the foundations of business dealings, each type of lawyer plays a vital role in upholding justice and navigating the intricate web of laws.
Public Interest Advocates embody the spirit of social justice, fighting for those who may otherwise be left unheard, while Family Advocates provide essential support and guidance in the personal and emotional realm of family law. Environmental Advocates stand as guardians of our planet, and Technology Advocates navigate the cutting edge, ensuring that our legal systems evolve alongside our increasingly digital world.
The synergy between these different types of lawyers forms a robust legal ecosystem, one that adapts to the evolving needs of individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the legal landscape, it is essential to appreciate the dedication, expertise, and unique contributions of each type of lawyer.
Ultimately, whether they stand before a judge, negotiate behind closed doors, or advocate for change on a broader scale, lawyers are united by a common purpose—to serve justice and uphold the principles that form the foundation of our legal system. The variety of legal advocates we’ve explored today highlights the vast array of challenges our society faces and the specialized expertise required to meet them.
As we move forward, let us acknowledge and celebrate the diverse talents within the legal profession, recognizing that each type of lawyer, in their own way, contributes to the pursuit of a fair and just society. Through collaboration and understanding, these legal professionals collectively shape the course of justice and contribute to the ongoing evolution of our legal systems.
Author
Aditi Parwal